Edu News | November 25, 2018
Educator Game Plan: InSight Mars Landing and Beyond!
UPDATE: Nov. 27, 2018 – The InSight spacecraft successfully touched down on Mars just before noon on Nov. 26, 2018, marking the eighth time NASA has succeeded in landing a spacecraft on the Red Planet. This story has been updated to reflect the current mission status. For more mission updates, follow along on the InSight Mission Blog, JPL News, as well as Facebook and Twitter (@NASAInSight, @NASAJPL and @NASA).
NASA's newest Mars mission, the InSight lander, touched down on the Red Planet just before noon PST on Nov. 26. But there's more work ahead before the mission can get a look into the inner workings of Mars. Get your classroom ready to partake in all the excitement of NASA’s InSight mission with this educator game plan. We’ve got everything you need to engage students in NASA's ongoing exploration of Mars!
Day Before Landing
- Read NASA/JPL Edu’s Teachable Moment, “NASA’s ‘Cyber Monday’ Mars Landing to Deliver Science Firsts,” to get a preview of the engineering and science involved in landing InSight and placing its instruments on Mars. Explore the related activities and resources in the “Teach It” and “Explore More” sections.
Landing Day (Nov. 26)
- Check out The Oatmeal’s webcomic for an explainer of how the InSight mission will land on Mars, what it will do on the planet and what it's hoping to find out.
- Watch these fun, one-minute videos for a quick overview of how landing sites are chosen, how spacecraft get to Mars, and what it takes to land there.
- Have students read about JPL’s “landing-site dude” and his rotating cast of interns, who have helped select seven of NASA’s Mars landing sites – including InSight’s!
- Have students read the JPL news release “How Will We Know When InSight Touches Down?”
- Watch live commentary as a class and follow along on the InSight Mission Blog, as well as Facebook and Twitter (@NASAInSight, @NASAJPL and @NASA) using #MarsLanding.
Next Day
- Review the Teachable Moment to find out what needs to happen before InSight’s science operations can begin. Then create an instructional plan with these lessons, activities and resources that get students engaged in the science and engineering behind the mission.
- Check out InSight’s first images from Mars, here. (This is also where you can find raw images from InSight throughout the life of the mission.)
Over the Next Month
- Watch these “Mars in a Minute” videos to find out what InSight is hoping to learn on the Red Planet: “What’s Inside Mars?” “Are There Quakes on Mars?” And “How Did Mars Get Such Enormous Mountains?”
- Have students explore NASA’s Experience InSight interactive to learn about InSight’s science instruments and how each will be deployed to the surface of Mars.
- Follow along on the InSight Mission Blog and @NASAInSight social media over the next few weeks as NASA gets to work surveying the landing site and determining where to place each of the instruments.
- Try the lessons and activities below with students to get them doing some of the same science and engineering as InSight:
-

Robotic Arm Challenge
In this challenge, students will use a model robotic arm to move items from one location to another. They will engage in the engineering design process to design, build and operate the arm.
Grades K-8
Time 30 mins - 1 hr
-

*NEW* Exploring the Colors of Mars
Students use satellite and rover images to learn about the various features and materials that cause color variation on the surface of Mars, then create their own “Marscape.”
Grades 2 and 5
Time 1-2 hrs
-

*NEW* Planetary (Egg) Wobble and Newton's First Law
Students try to determine the interior makeup of an egg (hard-boiled or raw) based on their understanding of center of mass and Newton’s first law of motion.
Grades 3, 6-8
Time 30 mins - 1 hr
-

Touchdown
Students design and build a shock-absorbing system that will protect two "astronauts" when they land.
Grades 3-8
Time 30 mins - 1 hr
-

Mission to Mars Unit
In this 19-lesson, standards-aligned unit, students learn about Mars, design a mission to explore the planet, build and test model spacecraft and components, and engage in scientific exploration.
Grades 3-8
Time Varies
-

*NEW* Heat Flow Programming Challenge
Students use microcontrollers and temperature sensors to measure the flow of heat through a soil sample.
Grades 5-12
Time 1-2 hrs
-
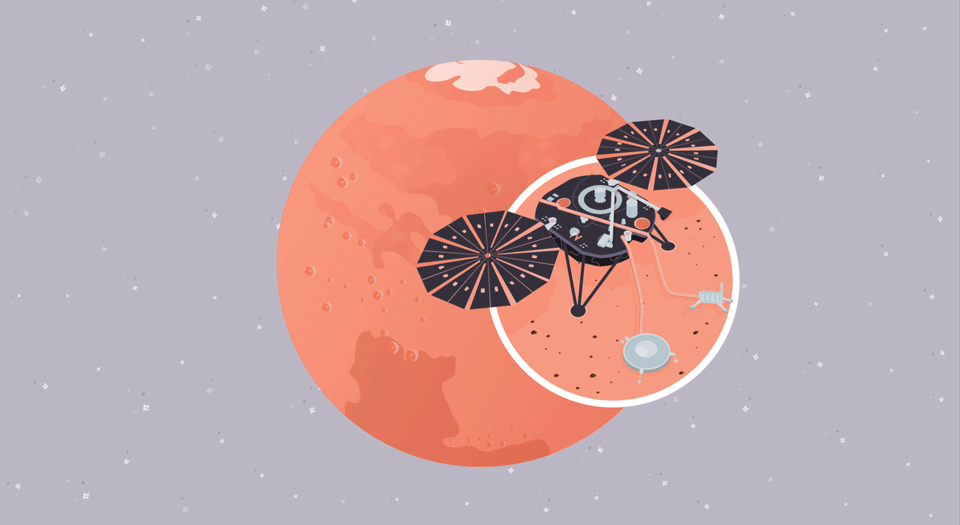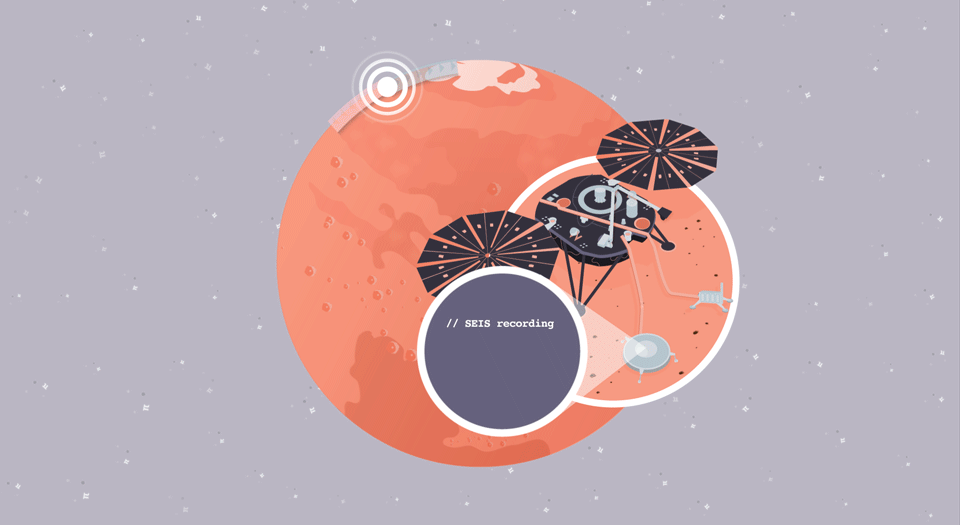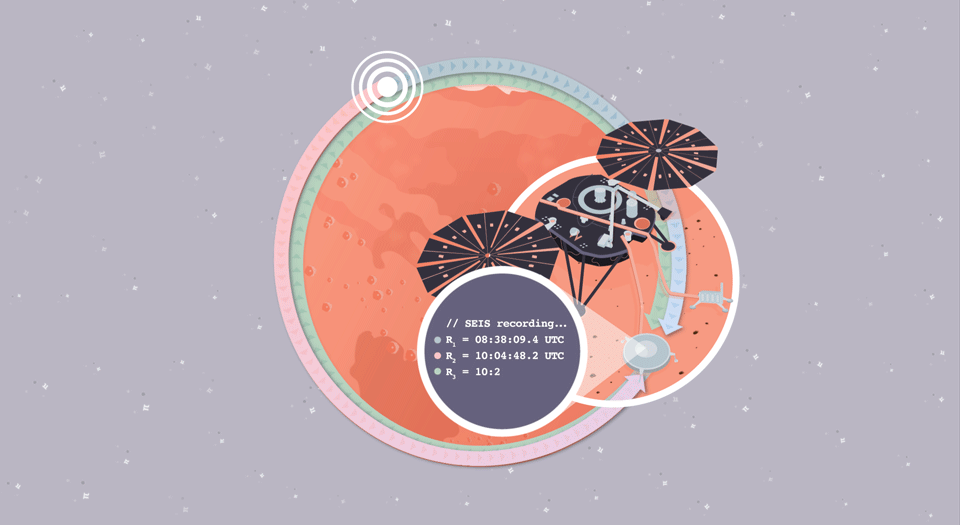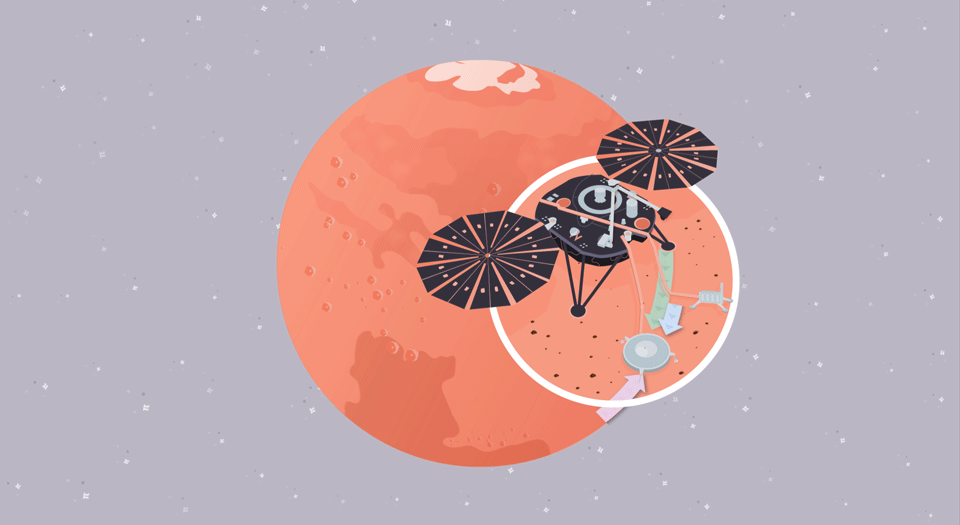
Quake Quandary
In this illustrated math problem, students use the mathematical constant pi to identify the timing and location of a seismic event on Mars, called a "marsquake."
Grades 11-12
Time Less than 30 mins
Explore More
Follow Along
Resources and Activities
- Teachable Moment: NASA InSight Lander to Get First Look at ‘Heart’ of Mars
- InSight Lessons
- Mars Lessons
- Mars Activities for Students
Feature Stories and Podcasts
- InSight Podcast: "On a Mission"
- "The 'Claw Game' on Mars Plays to Win" – Oct 16, 2018
- "NASA's InSight Will Study Mars While Standing Still" – Oct. 24, 2018
- "The Mars InSight Landing Site is Just Plain Perfect" – Nov. 5, 2018
Websites and Interactives
TAGS: InSight, Mars Landing, Educators, K-12, Elementary School, Middle School, High School, Lessons and Activities, Educator Resources, Mars
Edu News | April 23, 2015
JPL Role Models and Rovers Promote STEM for Girls
On a recent school night, seven enthusiastic female engineers and scientists from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, rolled into Santa Clarita, armed with three eight-wheeled Mars rover models. Their mission: to encourage hundreds of junior high and high school girls to reach for the stars in their education and future careers. Their strategy: to pique the girls' interest with an event called "Women in STEM: Going to Mars and Beyond!"
The evening featured rover races, demos and encouragement from the JPLers, who told the girls, "You, too, can do what we do someday."
There was definitely an audience for a message like that. Within five days of being advertised online, the March 18 event at Golden Valley High School "sold out," with 550 free tickets distributed and a waiting list cut off after 90 people.
"This just shows that people are hungry for events where girls can learn about STEM careers and consider them as an option," said Dennis Young, who works on the Mars Curiosity rover mission at JPL. Young, a longtime Santa Clarita resident, initiated and organized the event. His motivation was to expose his young daughter and other girls like her to career opportunities in STEM - science, technology, engineering and math - in the same way as his son and other boys. He had the blessing of Curiosity Project Manager Jim Erickson, who said, "I'm happy to support our team in fostering interest in STEM by young people."
The event was a collaboration between JPL and the William S. Hart Union School District. Janis Fiock, the district's college and career advisor, said she was thrilled when Young first proposed the event to her. "I recognize that women are under-represented in STEM careers. Girls need exceptional role models such as the women scientists and engineers from JPL to encourage them to move forward with their goals. They need to know that it's 'cool' to be smart."
Among the role models participating that night was Mars Curiosity Deputy Project Manager Jennifer Trosper, who also lives in Santa Clarita. Trosper had already teamed up with Young for previous community outreach and education events. She eagerly agreed to speak at the Women in STEM event, as did the six other speakers. Trosper's presentation included hands-on demonstrations, such as asking a young girl to jump as high as she could, then showing her with a tape measure how much higher she could jump under the lesser gravity of Mars.
One common theme ran through all the personal stories shared by the JPL speakers: STEM is not just for boys. Mechanical engineer Jackie Lyra explained that as a child in Brazil, she was literally told the opposite - that engineering school was only for boys. But she ended up studying in the U.S. and ultimately working at JPL, where she has been involved in landing four rovers on Mars, including Curiosity.
Lyra believes that because girls are generally not exposed to STEM topics as often as boys, the subject matter might seem intimidating to some, and they might be afraid to fail. She tried to drive home the point that it's okay to fail, as long as you learn from your mistakes and try again.
Looking back on the evening, Trosper recalls one particular conversation with a girl that reminded her why it's important to promote STEM opportunities. The girl had previously been told at a career fair that she should pursue a job in sales because she was pretty and could make a lot more money.
"This turned her off to engineering, even though she had dreamed of building a spacecraft to capture space junk and designing rocket engines to travel to distant stars," Trosper said. "Her mother dragged her to our STEM event to see if her interest in space could be sparked again." Trosper hopes she encouraged the girl to pursue her dreams, whatever they are, and not to let anyone else tell her what her talents or interests should be. "Besides, I told her I probably make more money than many people in sales."
Lyra brought up that same point in her presentation, throwing out a few numbers to demonstrate that the girls can potentially make more money in STEM. She asked the audience "Who wants to make $280 today?" After hands shot up throughout the auditorium, Lyra explained that STEM careers are not only fun and exciting, but lucrative as well -- a female fresh out of college could make about $75,000 a year with a bachelor's degree.
Other JPL speakers included Molly Bitner, just a few years out of college and working as a systems engineer, who told the girls she loves STEM, skydiving and chocolate; Victoria Davis, a chemist in the JPL battery group who lives in Santa Clarita and, in fact, introduced two local teachers who had pushed her toward excellence at Saugus High School; and Kim Lichtenberg, who, despite being the daughter of an astronaut and thinking she herself would not pursue a STEM career, eventually carved her own path in the sciences, with specialties such as analyzing Martian terrain.
Another JPLer, Shannon Statham, an aerospace engineer, described how she works with CubeSats -- "big satellites in small packages" and, in her free time, perfects salsa dancing. Diana Trujillo told the audience she spoke minimal English when she came to the United States from Colombia. She worked hard to become an engineer and now, at JPL, she "telecommutes" to Mars, as part of the team that sends computer commands to Curiosity.
During the course of the evening, the non-human guests also got their share of attention. The three Mars rover models arranged on the stage sprang into action at times, first when the girls joined in races with them. Then, the audience was invited to come up and get "rolled over" by a mini rover. The first volunteer was Hart School District Superintendent Vicki Engbrecht, who gamely went up on stage to have a rover "run over" her back. Once the ice was broken, the girls and their parents lined up to sprawl on a blanket so the rover could roll over them, too.
Young points out that, because numerous studies show that girls often hesitate to raise their hands and ask a question in a group setting, there was no formal Q and A. Instead, at the end of the event, there was a casual meet-and-greet, featuring the women of JPL standing near tables festooned with spacecraft parts, brochures and stickers.
As the audience filed out afterwards, smiles were clearly visible on the faces of the students, parents and JPL participants.
Young has heard from grateful parents who were thrilled that their daughters were able to meet real-life female role models from JPL. But he thinks perhaps the ultimate measure of success came during the program, while the JPL women were speaking. He watched the audience closely and did not see even one girl looking down at a cell phone or texting.
For more information about hiring JPL speakers for your classroom or group, visit the JPL Speakers Bureau page.
To hear more inspirational stories from female engineers and scientists at JPL, visit the Women at JPL website.
TAGS: STEM, Women in STEM, High School, Middle School, Elementary School, Women at NASA
Edu News | September 27, 2013
NASA Websites Merge Science Standards, Content
Educators can now find an extensive list of NASA classroom activities, games and quizzes that align with the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) released this year and already adopted in California and several other states.
Interactive lists on the NASA Space Place, Climate Kids and SciJinks websites define the concepts under each of the three NGSS dimensions -- disciplinary core ideas, science and engineering practices, and crosscutting concepts -- and link directly to the related educational content on those sites. The lists can be sorted by subject or grade level.
The new resource lets educators easily build lesson plans that meet the new standards, which now include concepts like climate change science, engineering design and natural hazards, and also engage students in NASA missions and science.
The new tool is available on the Space Place, Climate Kids and SciJinks websites at:
http://spaceplace.nasa.gov/science-standards
http://climatekids.nasa.gov/science-standards
http://scijinks.gov/science-standards
To learn more about the Next Generation Science Standards, visit: http://www.nextgenscience.org











